Wind load calculation for solar structures
Need a wind study for solar panels?
In a world constantly seeking sustainable and renewable energy sources, solar energy has emerged as one of the most promising options. Solar panels, capable of converting sunlight into electricity, have experienced a fast adoption across various industries and households. However, to maximize their efficiency, one must consider not only solar radiation but also the wind impact. Wind studies for solar panels play a crucial role in the proper design and installation of photovoltaic systems, ensuring optimal performance and sustainable energy production.
Wind studies are essential in the planning and development of solar energy systems. While sunlight is the primary source of energy for solar panels, wind can significantly impact their performance and longevity.
Key aspects of wind studies for solar panels
Optimization of location
Robust design
Cost reduction
Energy efficiency
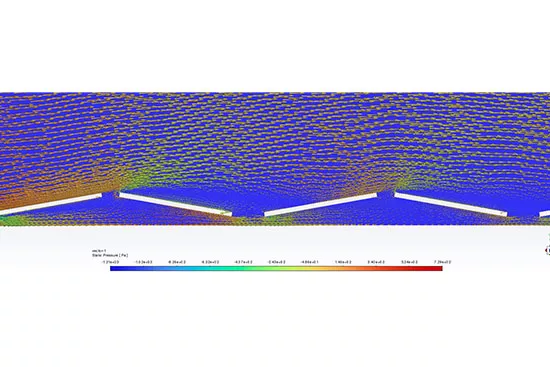
Wind flow lines on solar panels
Methods used in wind studies for solar panels
Wind studies employ various techniques to assess the influence of wind on photovoltaic systems. Some of the most common methods include:
- Climatic data analysis: Historical climatic data from the specific location is used to estimate wind speed and direction during different times of the year.
- Computational modeling: A specialized software is used to perform computational simulations to analyze wind flow around solar panels and surrounding structures.
- Field measurements: Direct wind measurements are conducted at the installation site to obtain precise and local data on wind conditions.
- Wind tunnel testing: In some cases, wind tunnels are used to simulate specific conditions and assess the behavior of the system under extreme situations.
Contact us
Basic information on data protection
Responsible: Cero Metros Cuadrados, S.L.
Purposes: Manage the sending of information that you request. Sending commercial communications.
Legitimation: Consent. You can withdraw consent at any time.
Recipients: Your data will not be transferred to third parties except in case of legal obligation.
Data subject's rights: To access, oppose, rectify and have their data deleted, as well as other rights as explained in the additional information.
You can access additional and extended information at this link.

